GREENLIGHT_REDCAT
Towards a Greener Reduction Chemistry by Using Cobalt Coordination Complexes as Catalysts and Light-driven Water Reduction as a Source of Reductive Equivalents
Project description
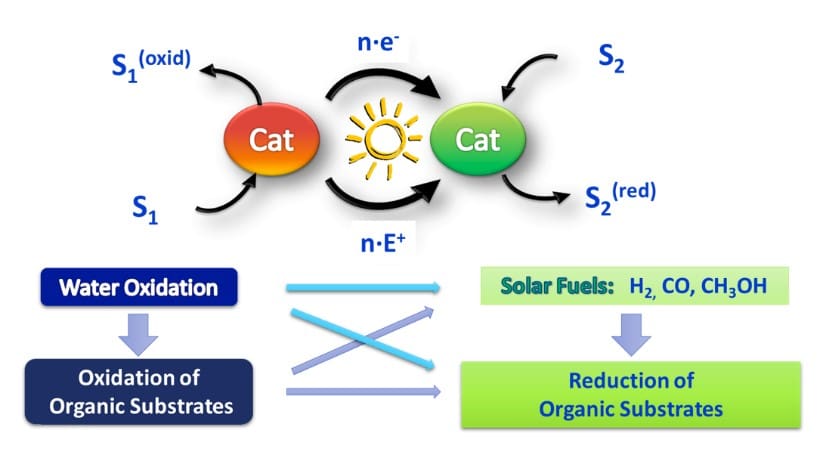
This project entails the use of visible light as driving force and water as a source of hydrides for the synthesis of high-value chemicals. The development of alternative greener synthetic methods to transform renewable feedstocks into elaborated chemical structures mediated by solar light is a prerequisite for a future sustainable society. In this regard, this project entails the use of visible light as driving force and water as a source of hydrides for the synthesis of high-value chemicals.
The project merged photoredox catalysis with 1st row transition coordination complexes catalysis to open a new avenue for greener selective catalytic reduction processes for organic substrates. The ground-breaking nature of the project has been:
A) Develop light-driven region- and/or enantioselective catalytic reductions using well-defined cobalt coordination complexes with aminopyridine ligands, initially developed for water reduction. Sterics, electronics and supramolecular interactions (apolar cavities and chiral pockets) will be studied to proper control of the selectivity in the reduction of i) C=E and C=C bonds and ii) in the C-C inter- and intramolecular reductive homo- or heterocouplings.
B) Fundamental understanding of the light-driven cobalt catalysed reductions characterizing intermediates that are involved in the reactivity, kinetics and labelling studies as well as performing computational modelling of reaction mechanisms. The basic understanding of operative mechanisms has expedited a new methodology for electrophile-electrophile umpolung couplings.
C) Enhance catalytic performance of the light-driven cobalt catalysed reductions by self-assembling of catalystphotosensitizer into carbon based pi-conjugated materials through noncovalent supramolecular interactions. Likewise, it has allowed electrode immobilization for electrocatalysed reductions using water as a source of protons and electrons.
As a proof of concept, cobalt catalysts based on aminopyridine ligands have been shown highly active in the light-driven reduction of ketones and aldehydes to alcohols, using water as the source of hydrogen atom.

This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 648304.
-
Reference: 648304
-
Call identifier: H2020-ERC-2015-CoG
-
Timeline
01/07/2015 - 30/06/2020
-
ICIQ's Budget
1,999,063 € -
Principal Investigator
Prof. Julio Lloret-Fillol
-
Financing agents
ERC Consolidator Grant, Horizon 2020

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements