Toward an informative comparison of heterogeneous, synthetic, and biological electrocatalysis in energy conversion
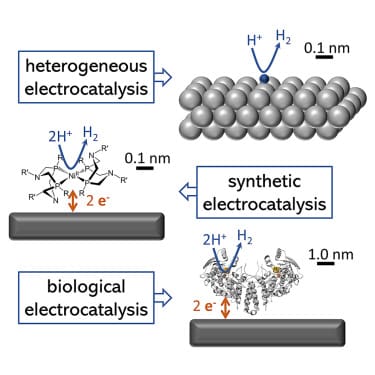
An urgently needed transition toward a sustainable and renewable energy landscape compels an increasing role for electrocatalysis. Distinct classes of electrocatalysts have each shown important benefits in energy conversion and the activation of small molecules such as CO2, H2O, O-2, and H-2: synthetic and biological molecular electrocatalysts and heterogeneous and reticular material electrocatalysts. This perspective seeks to foster knowledge exchange between the scientific communities by comparing these different electrocatalytic systems. The different subdisciplines employ divergent nomenclature, analytical approaches, and definitions of catalytic activity, even in cases of substantial overlap in chemical principles. We propose a set of conditions that must be met to ensure an unbiased comparison. Through sustained efforts to share best practices and harmonize approaches, we anticipate enhanced collaboration among subdisciplines, thereby facilitating innovative thinking and advancing the field of electrocatalysis toward its full potential in contributing to a sustainable and renewable energy future.
Jeuken, L. J. C.; Hetterscheid, D. G. H.; Koper, M. T. M.; Casadevall, C.; Leger, C.; Llobet, A.; Milton, R. D.; Nakamura, R.; Tschulik, K.
Chem. Catalysis 2024, 4, (10), 101098
DOI:
10.1016/j.checat.2024.101098
Associated ICIQ research group/s:
-
RESEARCH GROUP/S
Prof. Antoni Llobet
-
RESEARCH GROUP/S
Dr. Carla Casadevall

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements




















