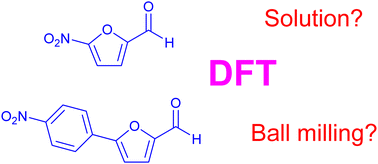
Computational study on the mechanism for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients nitrofurantoin and dantrolene in both solution and mechanochemical conditions
A combination of density functional theory (DFT) calculations and microkinetic simulations is applied to the study of condensation between N-acyl-hydrazides and aldehydes in acidic media to produce the active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) nitrofurantoin and dantrolene. Previous experimental reports have shown that the use of ball milling conditions leads to a reduction in the reaction time, which is associated with a significant reduction of waste. This result is reproduced by the current calculations, which additionally provide a detailed mechanistic explanation for this behavior. Computational chemistry is able to reproduce and explain experimental reaction times for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients nitrofurantoin and dantrolene both in solution and ball milling conditions.
Galeas, D. M.; Tolbatov, I.; Colacino, E.; Maseras, F.
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, (37), 24288-24293
DOI:
10.1039/d4cp01613k

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements



















