ICIQ Open Science
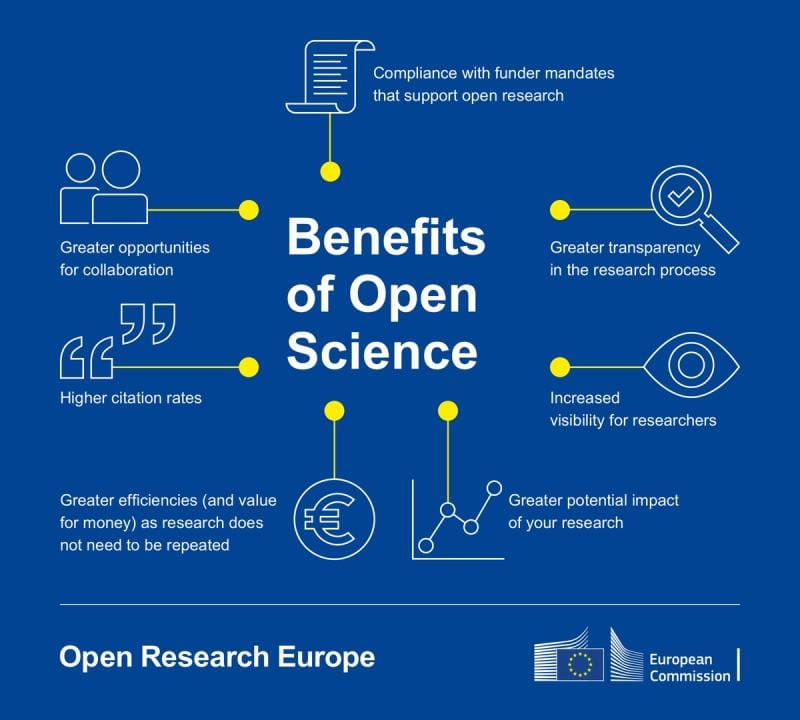
ICIQ recognises the outmost importance of sharing knowledge among peers and citizens to maximise the impact of our activities, which catalyses the changes our staff envision for our community. The institutional Open Science Policy and the internal Guidelines on Open Access & Data Management are the basic documents to instruct our scientific activities in the following years, aiming to align the center’s actions with the main strategies and legislation applicable to its current research ecosystem.
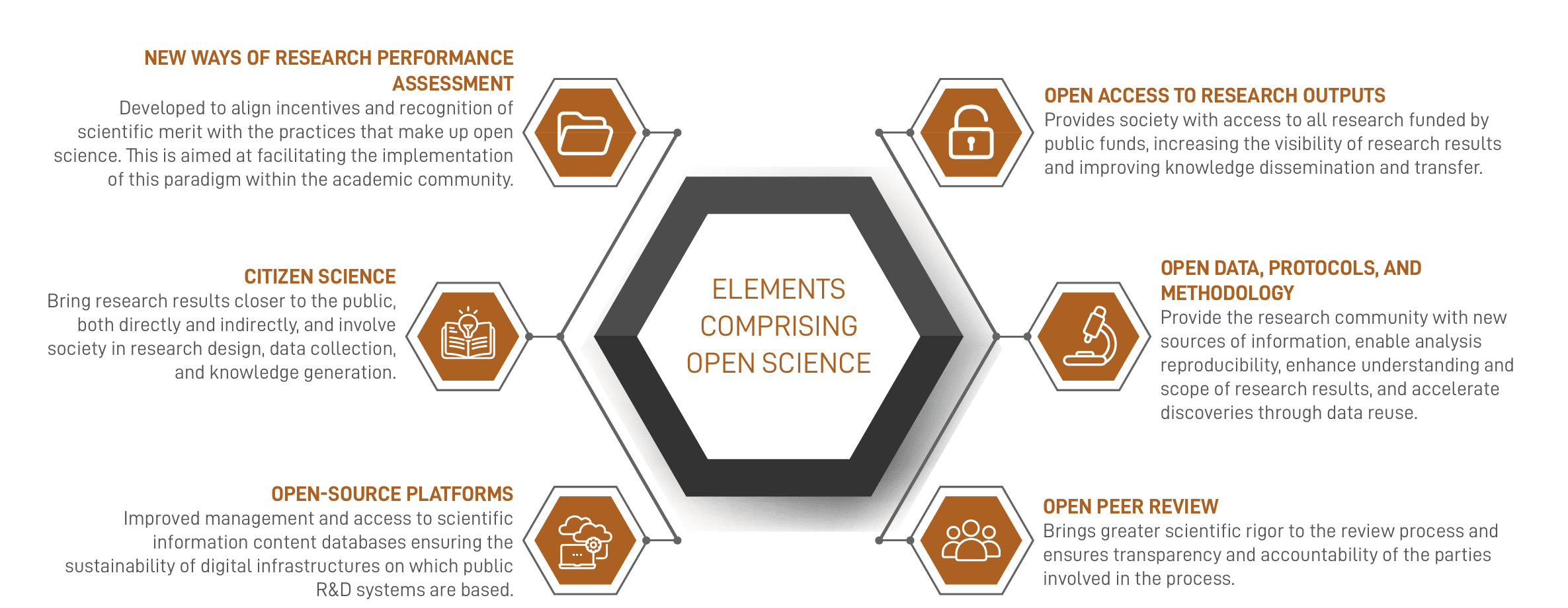
Elements comprising Open Science
-

Research Performance
Assesment -

Open Access to
Research Outputs -
Open data, protocols
and Methodology -

Citizen Science
-

Open Peer Review
-

Open-Source
Platforms
Strategic documents and Regulations
-

UNESCO Recommendation on Open Science
-

Open Science in Horizon Europe
-

HE Programme Guide (Point 16. Open Science)
-

Model Grant Agreement for Horizon Europe (Article 17 & Annex 5)
-

Spanish National Strategy for Open Science (ENCA) 2023-2027
-
Catalan Open Science Strategy
-

CERCA Data Management Strategy
-

CERCA Code of Conduct
Open Repositories
-

RECERCAT. Dipòsit de la Recerca de Catalunya
Research literature of universities and research centres in Catalonia
-

CORA Research Data Repository
Federated and multidisciplinary data repository for the publication of FAIR datasets following the EOSC guidelines
-

Cambridge Structural Database
Comprehensive repository of validated curated small molecule organic and metal-organic crystal structures
-

iPublic | scimarina ICIQ
Tools for Researchers
-

eChemPad
ICIQ's repository of research data. Under development
-

eiNaDMP
Tool provided by CSUC to help researchers to create, review, and share data management plans that meet institutional and funder requirements
-

EOSC (European Open Science Cloud)
-

F-UJI FAIR assessment
Web service to programmatically assess FAIRness of research data objects
-

Journal Checker Tool
Web service to check publishing options supported by funder's OA policies
-

OpenAlex
Open catalog of the world's scholarly papers, researchers, journals, and institutions.
External Training and Resources
Citizen Science and Outreach
In addition to its commitment to providing open access to data and publications, ICIQ is dedicated to expanding the societal impact of its research by actively engaging in citizen science. We recognise that public involvement in scientific projects is crucial for making research more relevant and accessible.
ICIQ encourages its scientists to take an active role not only in citizen science initiatives but also in creating and sharing open educational resources, fostering a more collaborative and inclusive approach to scientific discovery.
> Learn more on our outreach section

FAQs

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements