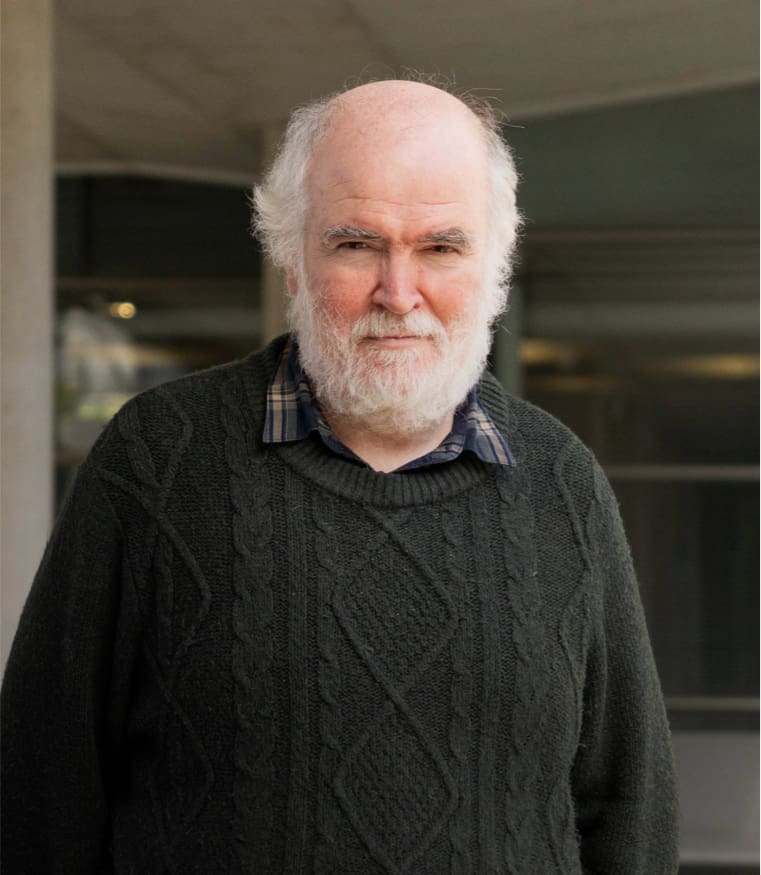
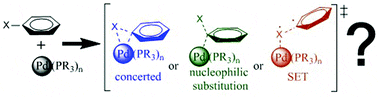
The diverse mechanisms for the oxidative addition of C–Br bonds to Pd(PR3) and Pd(PR3)2 complexes
The reaction between bromobenzene and palladium(0) complexes leading to a palladium(II) complex containing bromide and phenyl ligands is studied computationally with DFT methods. Three different mechanisms are considered: concerted, nucleophilic substitution and radical. A systematic analysis is carried out on the effect on each of these mechanisms of a number of variables: the identity of the phosphine (PF3, PH3, PMe3 or PPh3), the nature of the solvent (vacuum, tetrahydrofuran, dimethylformamide or water) and the number of phosphine ligands (mono- or bis-phosphine). The concerted and nucleophilic substitution mechanisms are competitive in many cases, the identity of the preferred one depending on a combination of factors. Additional calculations with bromomethane, bromoethylene and bromoethane are carried out in selected cases for further clarification.
Besora, M.; Maseras, F.
Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 16242-16248
DOI:
10.1039/C9DT03155C

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements



















