Technetium and Rhenium Auto-reduction, Polymerization and Lability towards Group VII Polyoxometalate Chemistry
Group VII Tc and Re have long been studied to develop both radiopharmaceuticals and technologies for nuclear materials management. Fundamental research has targeted understanding this periodic table crossroads where polyoxometalates meets metal-metal bonded complexes. Here we have isolated green hygroscopic and metastable crystals of (ReVI,oct)2(ReVII,tet)2(OH)2(O)12⋅H2O (ReVI,VII-green, tet=tetrahedral, oct=octahedral), determined by single-crystal x-ray diffraction. In addition to color, Re-L1 X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy confirms the reduced oxidation state. ReVI,VII-green provides the first demonstration of Re autoreduction, long-observed for Mn and Tc. We also isolated and structurally characterized [Tc4O4(H2O)2(ReO4)14]2− (Tc4Re14) polyanion crystals that contain Tc(V) and Re(VII), consistent with greater stability of reduced Tc compared to reduced Re. Small angle X-ray scattering of both compounds and prior-reported polyanion [Tc4O4(H2O)2(TcO4)14]4− (Tc20) dissolved in acetonitrile indicated a qualitative lability order of oxo-linkages of Re-O−Re > Re-O−Tc >Tc-O−Tc, and lability of Tc20 was also probed by 99Tc nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Computation provided insight into 99Tc chemical shifts as well as lability. Based on both reducibility and solution phase dynamics of polynuclear compounds investigated here, Re is an imperfect surrogate for Tc, and further expansion of group VII polyoxometalate chemistry seems promising.
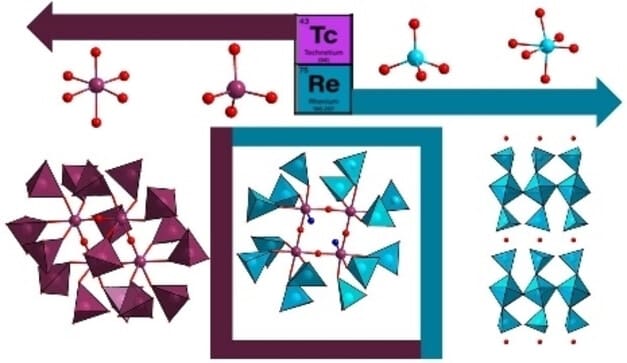
Bustos, J.; Shohel, M.; Buzanich, A. G.; Zakharov, L.; Buils, J.; Segado-Centellas, M.; Bo, C.; Nyman, M.
Chem. - Eur. J. 2025, e202404144
DOI:
10.1002/chem.202404144
Associated projects:
-
COMPLEXSIM
The COMPLEXSIM project aims to develop and apply new computational methods for studying complex reactive mixtures of metal oxide species in solution, such as those formed in the field of polyoxometalates. Based on our recently developed method, phase speciation diagrams (concentration vs. pH) of various heteropolyoxometalates, such as Keggin, Anderson, and Wells-Dawson anions, will be determined directly from DFT methods.
See more

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements






















