Photochemical C–H Borylation in Organic Synthesis
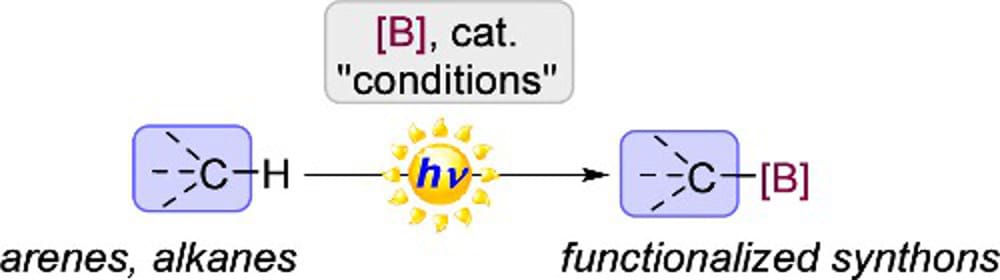
Although C–H bond functionalization has been extensively studied since its discovery in 1955, the borylation of organic compounds by activating C–H bonds only became popular since the valuable discovery by Hartwig in 1995 who considered a wider application of these transformations in synthetic organic chemistry. For C–H borylation, catalytic activation of this generally low-reactivity bond can be performed in many ways. Among the approaches reported are the use and application of stoichiometric reagents, thermal activation, and photochemical activation of suitable substrates. Iridium-, ruthenium-, and rhodium-based catalytic protocols using thermal activation have played a crucial role toward the establishment of this area. Photochemical activation, though, has only been scarcely explored despite the fact that it represents a comparably environmentally benign protocol using light as a renewable energy source. In this literature survey, we highlight the recent developments in photochemical C–H borylation from its initial inception up to the latest advancements.
Rej, S.; Amos, S. G. E.; Kleij, A. W.
ACS Catal. 2025, 15 (3), 1753–1770
DOI:
10.1021/acscatal.4c07169
Associated projects:
-
AVANT-GARDE
The AVANT-GARDE project aims to uncover new reactivity patterns and opportunities to transform vinyl-, alkynyl- and allene-appended heterocyclic substrates into stereodefined synthons with value in fine-chemical and pharmaceutical development programs. The key approximation is through the utilization of transition metal (TM) catalysis, and more specifically the use of (mostly) base metal (M = Ni, Co, Cu) and/or photocatalysts to assist these protocols. The project builds on the previous and extensive experience of the Kleij group in the formation of sterically challenging stereocenters empowered by TM catalysis.
See more

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements






















