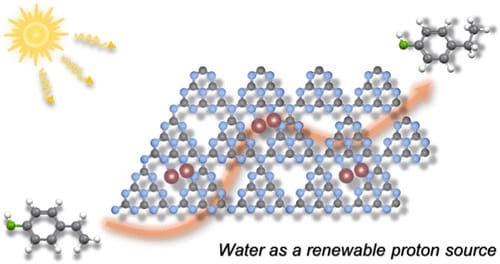
Diatomic Palladium Catalyst for Enhanced Photocatalytic Water-Donating Transfer Hydrogenation
Diatomic catalysts (DACs) present unique opportunities for harnessing ensemble effects between adjacent metal atoms, thus, expanding the properties of single-atom catalysts (SACs). However, the precise preparation and characterization of this type of catalyst remains challenging. Following a precursor-preselected strategy, here, we report the synthesis of a carbon nitride-supported Pd-DAC, which achieves an excellent yield of 92% for photocatalytic water-donating transfer hydrogenation of 4-vinylphenol to 4-ethylphenol, far exceeding that of other metal species, including Pd single atoms (47%) and nanoparticles (1%). Combining transmission electron microscopy with standardized machine learning atom-detection methods confirms the stabilization of a substantial fraction of dimeric Pd species over carbon nitride. Density functional theory (DFT) simulations associate the outstanding performance of Pd-DAC to enhanced substrate activation in the hydrogenation path compared to Pd-SAC. The work provides criteria for DACs characterization and demonstrates a transfer hydrogenation application that is sustainable and eco-friendly over conventional hydrogenation technologies.
Zhao, E.; Morales-Vidal, J.; Yang, Y.; Mitchell, S.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.-M.; Haw, S.-C.; Chan, T.-S.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Z.-J.; López, N.; Pérez-Ramírez, J.; Chen, Z.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147 (2), 2029-2036
DOI:
10.1021/jacs.4c15235
Associated projects:
-
SMELT
The specific objectives of SMELT are to describe stable, active and selective photo-electro-catalysts for industrially-appealing transformations that can be then applied to the search for optimized materials and/or rules to find new alternative formulations for catalysts with improved performance in terms of activity, selectivity and stability.
See more

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements