Conductive pencils
Objective: Performing the electrolysis of water using pencils as electrodes
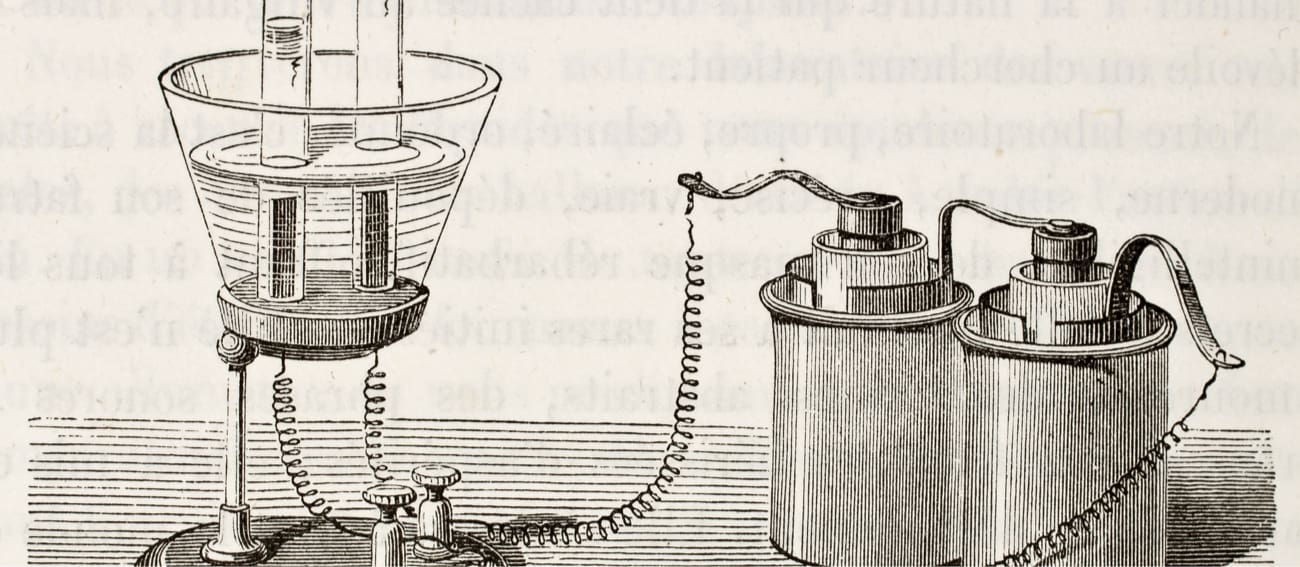
-
Laboratory materials
Beaker
Conducting wires with crocodile clips
9V battery
2 Pencils
Cardboard
Tablespoon
-
Reagents
Water
Sea salt
-
Questions
What happens when the cables are connected to the battery?
Which reaction takes place?
Why is salt added?
Procedure
- Sharpen the two sides of the pencils and attach the wires to them using the crocodile clips.
- Fill the beaker with tap water and dissolve a tablespoon of see salt.
- Make two holes in the cardboard through which the pencils will pass (the ends where there are no wires).
- Place the cardboard with the pencils over the beaker and connect the free ends of the cables to the battery terminals.
- Observe what happens.
Theoretical explanation
Water (H2O) is a substance that can be decomposed into its elements, hydrogen and oxygen, through a chemical process. When electricity passes through water, both gases are produced, and that’s why we observe bubbles inside the beaker. This phenomenon is called electrolysis of water.
2 H2O 2 H2 + O2
Due to the low degree of ionization of water, its electrical conductivity is low. Salt is therefore added to increase the conductivity and allow the electrolysis of water to occur.

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements














