 13/03/2025
13/03/2025
 12:00 h
12:00 h
 ICIQ Library
ICIQ Library
- Lecturer: Dr. Kosei Yamauchi
- University: Kyushu University, Japan
- Invited by: Prof. Julio Lloret-Fillol
Cobalt-NHC Molecular Catalysts Promoting Hydrogen Evolution from Water with High Turnover Numbers and Frequencies
Abstract
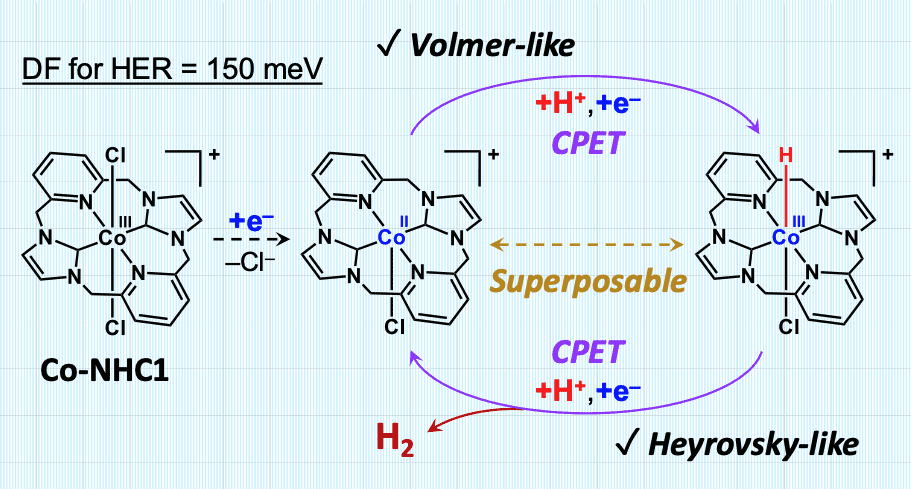
Energy conversion based on H2 evolution from water [1] and CO2 reduction into various chemicals [2-3] are the key technologies to solve the global warming and shortage of fossil fuels. It is also important to couple these reduction reactions with water oxidation [4] to convert solar energy into chemical energy. In this context, we have previously studied on molecular photosystems in which HER is driven by oxidative quenching of [Ru*(bpy)3]2+. The photosystem comprises of EDTA, [Ru(bpy)3]2+, electron relay and the catalyst, where one-electron-reduced species of methylviologen MV2+ (i.e., MV+•) only has a driving force (DF) of 150 meV for HER at pH 5.0. Within these studies, we succeeded in demonstrating that a macrocyclic cobalt-NHC complex Co-NHC1 (NHC: N-heterocyclic carbene) serves as a catalyst for HER using MV+• as a reductant. This is the first example of the 1st row transition metal complex showing the catalysis in this system. In addition, experimental and DFT results also reveal that a unique double CPET pathway is taken to evolve H2 by Co-NHC1 with substantially minimized reorganization energies [1]. This pathway can be viewed as related to the so-called Volmer-Heyrovsky mechanism adopted by some metals and is quite unique to Co-NHC1. Meanwhile, we have recently conducted the detailed analyses on the electrocatalysis of Co-NHC1 for hydrogen evolution from water. Importantly, the catalytic rate by Co-NHC1 has turned out to be extremely high even in neutral aqueous media. Our recent finding includes the development of the highly efficient molecular system in photochemical H2 evolution from alkaline water, which will be discussed in the presentation.
[1] K.Yamauchi*, K. Kawano, K. Yatsuzuka, K. Kawamura, M. Kan, K. Sakai*, Am. Chem. Soc., 2025, 147, 5602-5614 (Supplementary Cover).
[2] Lee, K. Yamauchi*, K. Sakai*, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 31597-31611.
[3] Liao, K. Yamauchi*, K. Sakai*, ACS Catal., 2024, 14, 11131-11137.
[4] Aimoto, A. R. Parent*, K. Yamauchi*, K. Sakai*, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146, 16866-16877.
Other events

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements




















