Englerin derivatives for treatment of cancer
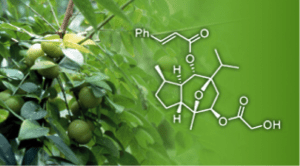
Disclosed is a compound of formula (I) in which a, R1- R5 and X1 are as described herein. Also disclosed are a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound and a method of using the compound for treating cancer, such as renal cancer.
Description of solution
The present invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of the invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
In one possible mechanism, englerin A activates transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) ion channels on kidney cancer cell surfaces, thereby increasing the influx of Ca2+ and killing the cancer cells (Akbulut et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54, 3787-3791). However, more recently, Beech has shown that sodium influx, not calcium influx, kills the cancer cells (Muraki et al., Scientific Reports, 2017, 7, 16988). Englerin A has been shown to be an agonist of TRPC4/C5, but englerin A is lethal in rodents at doses required to activate the TRPC4 channel (Carson et al., PLoS One, 2015, 10(6), 1-21). It was surprisingly discovered that compounds of formula (I) are therapeutically active in killing cancer cells, which was particularly unexpected, because the compounds of formula (I) were inactive as agonists of TRPC4. Without wishing to be bound by any theory, it is believed that TRPC4 agonism accounts for the lethality of englerin A. Because the compounds of formula (I) are not agonists of TRPC4, it is believed that the englerin analogs of formula (I) are less toxic to a subject in treating cancer. Accordingly, the present invention also provides a method of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject an effective amount of the compound.
Collaborators
Fundació Institut Catala d’Investigació Química (ICIQ), Universitat Rovira i Virgili (URV), University of Leeds, US Department of Health and Human Services, University of Delaware.
Funding
This invention was made with Government support under project number ZIA BC011470 05 funded by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (USA). The Government has certain rights in this invention.
License
Patent licensed to the National Institute of Health EEUU (NIH) and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) from USA.
-
Sectors of application
Health and pharma: treating diseases as cancer and renal cancer.
-
Inventors
John A. Beutler, Antonio Echavarren, William Chain, David Beech, Zhenhua Wu, Jean-Simon Suppo, Fernando Bravo, Hussein Rubaiy
-
IP situation
- Licensed to National Institute of Health EEUU (NIH) – National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- Patent PCT/US2018/040910
- Publication date: 19/01/2019

Empiece con un experto
Juntos, creemos un futuro más brillante brindando soluciones a través de una asociación.
Conecta con nosotros


















