A smarter way to predict chemical equilibria
New scaling protocol developed at ICIQ enhances predictions without experimental data
A research group led by Prof. Carles Bo at the Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ) has made a major step forward in predicting how certain chemical compounds, known as polyoxometalates (POMs), form. By developing a universal scaling protocol, the researchers have expanded the reach of their innovative tool, POMSimulator. This innovation, recently published in Digital Discovery, removes previous limitations and represents a key milestone in inorganic chemistry.
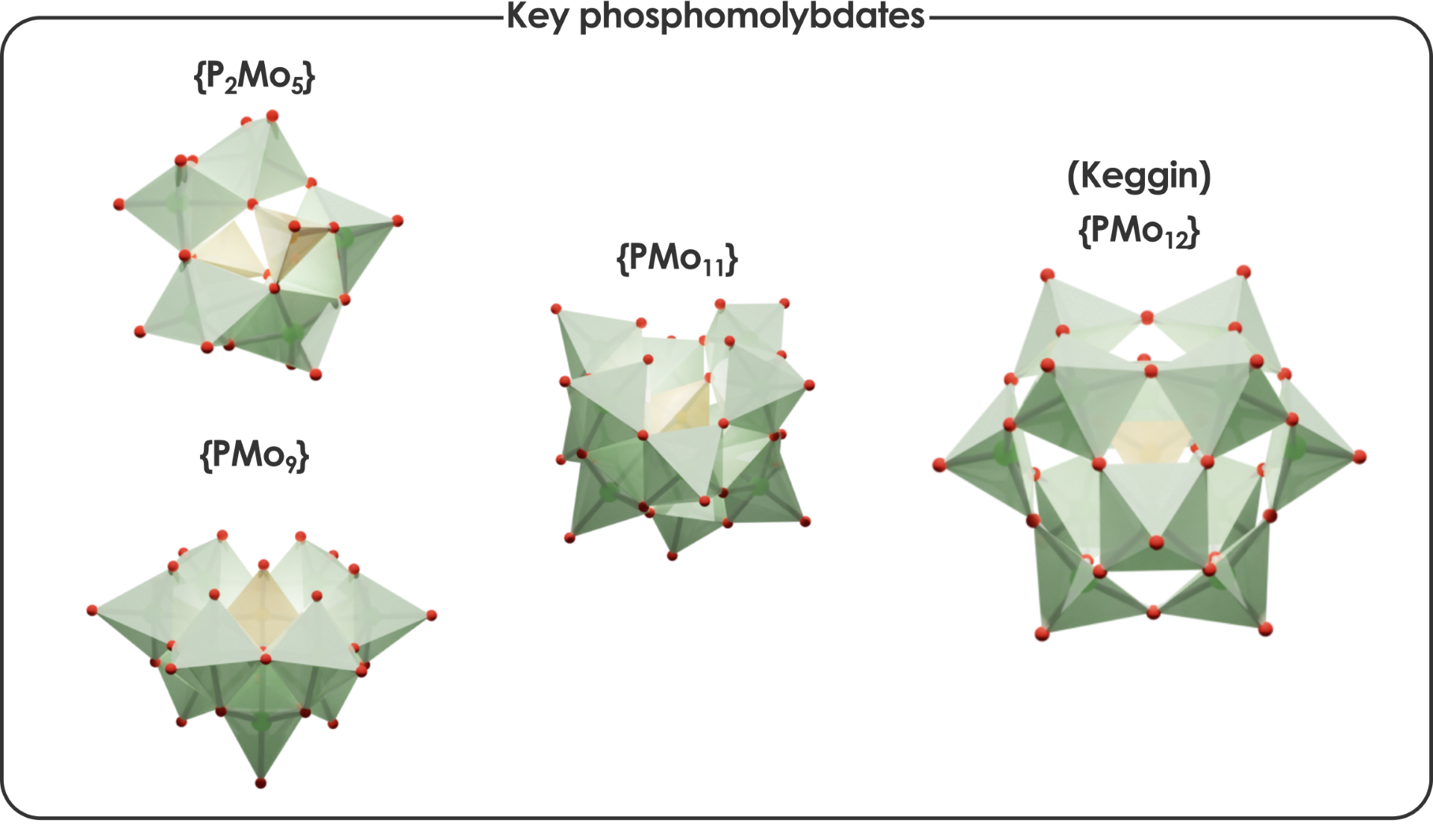
Predicting how molecules interact and change in different conditions is one of the big challenges in chemistry. One important aspect of this is determining equilibrium constants, especially acid dissociation constants (pKa), which are essential in fields ranging from biology to industry. However, predicting these values is particularly difficult for POMs, a group of molecular metal-oxo clusters that form through acid-base reactions.
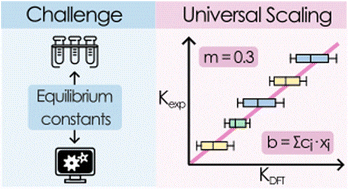
The researchers Dr. Jordi Buils, Dr. Diego Garay-Ruiz, Dr. Enric Petrus, Dr. Mireia Segado-Centellas, and Prof. Carles Bo have significantly improved POMSimulator, a tool they developed to simulate how POMs form. This method uses advanced quantum chemistry calculations, specifically Density Functional Theory (DFT), to model the chemical behavior of these compounds. By carefully analyzing a large dataset of POM formation constants, the researchers have introduced a universal scaling approach that fine-tunes the accuracy of predictions. Previously, POMSimulator relied on experimental data to adjust its predictions, but the new method eliminates this dependency, making it useful for systems where no prior data is available. The team has also introduced a statistical approach to deal with the huge amounts of data generated by the method, making the tool even more versatile.
How POMSimulator Works
The group of Prof. Bo presented in 2024 an open–source software package named POMSimulator that helps in understanding the formation mechanisms of POMs. By releasing a public version of the code, the researchers aimed to provide a tool for complementing the discovery of novel POMs, as POMSimulator predicts how POMs behave in water by running advanced computer simulations.
The process starts by collecting key molecular data, such as structures, electron densities and energy values, which are then used to build a chemical reaction network (CRN) automatically. This network, which describes how different molecules interact, is typically very complex. To make sense of it, the researchers developed a method which breaks the network down into manageable sets of equations. Solving these equations provides a detailed picture of how the molecules exist and interact in solution, including how pH levels affect their stability.
Impact and Future Applications
The innovation presented at Digital Discovery is the result of nearly seven years of dedicated research, including three PhD theses and six high-impact scientific publications. Prof. Carles Bo emphasizes the significance of this work:
“This paper represents the pinnacle of our group’s work over the past years, and I couldn’t be prouder. We have developed a novel computational method to simulate complex chemical equilibria, considering pH and species concentrations through DFT calculations—something no other method achieves. Our team, composed of young and brilliant researchers, has carried out all theoretical and computational work independently at ICIQ, demonstrating the power of data-driven research and coding skills in modern chemistry. Software drives the world!”
The improved POMSimulator methodology, along with its new universal scaling protocol, could be applied to many other chemical systems beyond POMs. With multiple published studies and ongoing research, this innovative tool has the potential to transform how scientists predict chemical equilibria, opening new doors for developments in catalysis, energy materials, and other fields.
Author Dr. Enric Petrus Pérez (2020)
Related news

Let's create a brighter future
Join our team to work with renowned researchers, tackle groundbreaking
projects and contribute to meaningful scientific advancements






 22-01-2025
22-01-2025