Diazomethylation reagent and process for using it
Currently, drug discovery and development are long-lasting processes with high associated costs, which has a significant impact on the price and accessibility of new marketed drugs. Furthermore, more than two-thirds of prescription drugs are chiral, with the majority of new chiral drugs being single enantiomers. A major obstacle to their discovery and development is associated with complex multi-step synthesis. In this sense, novel strategies that permit the synthesis of such drugs in a direct and efficient manner are required in order to meet the demands of the pharmaceutical industry. Late-stage C−H functionalization in the lead optimization phase has the potential to solve this problem; however, this process remains as a long-standing challenge in synthesis. That’s where this technology offers a solution.
Description of solution
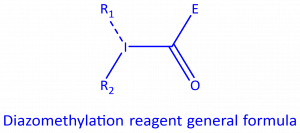
The research group of Dr. Marcos Garcia-Suero at ICIQ is focused on the development of new catalytic C−H & C−C functionalization strategies for chemical synthesis. The group has developed a new class of reagents for the diazomethylation of (hetero)aromatic substrates through the generation of carbynes, leading to the regioselective introduction of carbenoid groups in the reaction substrate. The developed diazomethylation reagent consists in a hypervalent iodine reagent useful in the insertion of the diazocarboxylate moiety into (hetero)aromatic C-H bonds through a Ru(II) mediated photoredox process. The introduced carbenoid group can further be functionalized by modification of the diazo group and/or the ester functional group to introduce molecular diversity.
The diazomethylation reagents are hypervalent iodine compounds wherein a diazomethyl group is appended to the iodine atom. Despite the presence of the diazo group, these compounds have proven rather stable in our hands (handled at room temperature and at small scale). These reagents are suitable for the transfer of the diazomethyl group under photoredox conditions to an aromatic C-H bond with excellent regioselectivity.
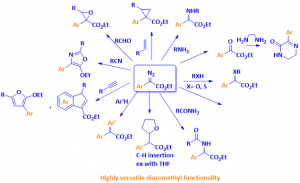
The diazomethyl functional group represents a good starting point in the preparation of compounds with high molecular diversity from one sole starting material, since it acts as a carbenoid, making it suitable for applications in the discovery and development of biologically active molecules, such as agrochemicals and drugs.
Given the innate ability of carbynes to form three new covalent bonds sequentially, Professor Marcos Garcia Suero and colleagues anticipated that a catalytic method of generating carbynes or related stabilized species would allow what they term an ‘assembly point’ disconnection approach for the construction of chiral centers.
Advantages and unique selling points
- SYNTHETIC SHORTCUT: The diazomethylation reagents developed by Marcos Garcia Suero’s group offer a solution to performing reactions that would otherwise require multi-step reaction procedures, being able to transform C-H bonds in highly versatile diazomethyl functionality, which subsequently can be transformed in a chiral stereogenic center bearing pharmacophore groups or diverse functional groups.
- HIGH REGIOSELECTIVITY: These reagents allow performing the diazomethylation reaction with high regioselectivity under mild conditions, using photoredox catalysis at room temperature. The photoredox reaction is mediated by blue light and a Ru(II) photosensitizer.
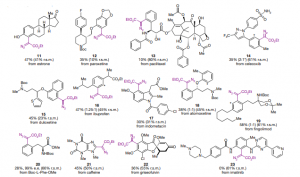
- FUNCTIONAL GROUP TOLERANCE: The developed methodology proved efficient even when the reaction substrate bears functional groups and could successfully be implemented onto pharmaceutical active ingredients.
- MILD CONDITIONS: The reaction takes place at room temperature under irradiation of blue light, in the presence of a catalytic amount of a Ru(II) photosensitizer, and in the presence of sodium bicarbonate as a base. This further facilitates the use of functionalized reaction substrates, such as active ingredients.
- DIVERSIFICATION: The reaction product can easily be turned into a broad variety of compounds following standard chemical procedures. The transfer of a diazomethyl functional group equivalent to a carbyne allows a further derivatization of the diazo group, including halogenation, C-H insertion, O-H insertion, trifluoromethylation and carboamination. The diazomethylation reaction tolerates the presence of functional group on the reaction substrate.
Collaborators
Fundació Institut Català d’Investigació Química (ICIQ).
Funding
European Research Council (ERC-CoG 2019, 865554), Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI) of the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (EUR2019-103814, PID2019-104101GB-I00, Severo Ochoa Excellence Accreditation 2020–2023 -CEX2019-000925-S), ICIQ Foundation, and the CERCA Programme (Generalitat de Catalunya) are gratefully acknowledged for financial support. We thank the European Union for a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Individual Fellowship (101032589).
-
Technology status
A proof of concept has been achieved in a laboratory scale on active ingredients as substrates (functionalized molecules).
-
Sectors of application
Late-stage functionalization, chemical libraries, drug optimization, pharmacology, R&D chemicals, synthesis
-
Inventors
Marcos García Suero and Zhaofeng Wang
-
IP situation
- Application numbers: EP3360871A1 (granted) and US16/482,966 (granted)
- Application date: 8 February 2020

Get started with an expert
Together, let’s create a brighter future providing solutions through a partnership
Connect with us