Elephant toothpaste
Objective: The objective of this experiment is to carry out a reaction that produces a kind of foam commonly known as “elephant toothpaste” due to the quantity and texture of the resulting mixture

-
Laboratory materials
A 500 mL Erlenmeyer
A plastic container
2 graduated cylinders (50 mL)
2 funnels
-
Reagents
Hydrogen peroxide 30% (H2O2)
Potassium iodide (KI) 0.3 M (50 g KI in 1 L of deionized water)
Dish soap
Food coloring (red and blue)
-
Safety
Don't forget the gloves, lab coat, and safety goggles!!!
-
Questions
What is the role of the dish soap?
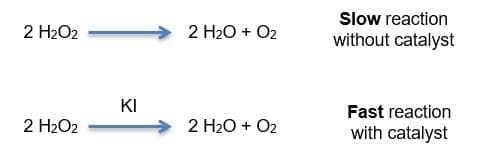
Which reaction takes place? Write it down.
What is a catalyst?
Procedure
- Using a graduated cylinder, measure 50 mL of hydrogen peroxide and pour it into the Erlenmeyer flask.
- Add two drops of red food coloring to the hydrogen peroxide and then slowly add blue food coloring along the sides of the Erlenmeyer flask (to simulate toothpaste).
- Add a squirt of dish soap.
- Using the other graduated cylinder, measure 50 mL of potassium iodide solution (KI, 0.3 M) and pour it into the Erlenmeyer flask.
Theoretical explanation
A catalyst is a substance that alters the speed of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. In this experiment, potassium iodide (KI) acts as a catalyst, accelerating the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, which generates oxygen and water as products. The gaseous oxygen, released rapidly due to the action of the catalyst, creates many bubbles when it comes into contact with the dish soap, forming the foam we call “elephant toothpaste.”
The hydrogen peroxide decomposition reaction is represented as follows: