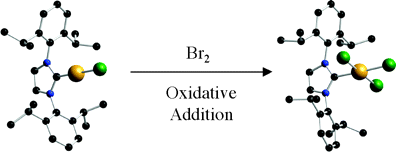
A series of (NHC)AuICl (1, NHC = N,N’-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene (IPr); 2, NHC = N,N’-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene (IMes); 3, NHC = N,N’-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imidazolin-2-ylidene (SIPr); 4, NHC = N,N’-bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)imidazolin-2-ylidene (SIMes); 5, NHC = N,N’-dicyclohexylimidazol-2-ylidene (ICy); 6, NHC = N,N’-diadamantylimidazol-2-ylidene (IAd); 7, NHC = N,N’-di-tert-butylimidazol-2-ylidene (ItBu)) complexes were reacted with LiBr to generate [(IPr)AuBr] (8), [(IMes)AuBr] (9), [(SIPr)AuBr] (10), [(SIMes)AuBr] (11), [(ICy)AuBr] (12), [(IAd)AuBr] (13), and [(ItBu)AuBr] (14). These (NHC)AuIBr complexes undergo oxidative addition of elemental bromine, leading to the new Au(III) complexes [(IPr)AuBr3] (15), [(IMes)AuBr3] (16), [(SIPr)AuBr3] (17), [(SIMes)AuBr3] (18), [(ICy)AuBr3] (19), [(IAd)AuBr3] (20), and [(ItBu)AuBr3] (21). Complete characterization by NMR spectroscopy and single-crystal X-ray diffraction were performed in order to discern structural differences between organogold(I/III) congeners. A preliminary study examining the activity of (NHC)AuIII species on the addition of water to alkynes is also presented.