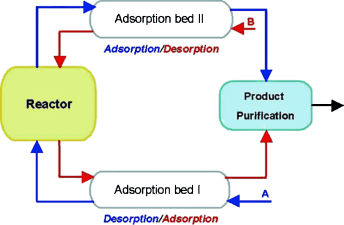
Supramolecular strategies, based on hydrogen bonds and ionic interactions, were investigated as tools for the recovery and recycling of homogeneous transition-metal catalysts by using reverse-flow adsorption (RFA) technology. The association (in solution) and adsorption (on support) of new functionalized host materials and phosphine guest ligands, functionalized with the complementary binding motifs, were fine-tuned for the application of these materials in a RFA reactor. The RFA technology for process-integrated recycling of homogeneous catalysts using these tailor-made phosphine ligands and silica-supported host materials resulted in a stable, semi-continuous catalytic system. Rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of methyl acetamidoacrylate and asymmetric hydrosilylation of acetophenone were studied as test reactions. Depending on the catalytic process the metal complex could be recycled several times without significant loss in conversion.