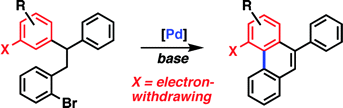
The regioselectivity observed in the intramolecular palladium-catalyzed arylation of substituted bromobenzyldiarylmethanes as well as theoretical results demonstrate that the Pd-catalyzed arylation proceeds by a mechanism involving a proton abstraction by the carbonate, or a related basic ligand. The reaction is facilitated by electron-withdrawing substituents on the aromatic ring, which is inconsistent with an electrophilic aromatic-substitution mechanism. The more important directing effect is exerted by electron-withdrawing substituents ortho to the reacting site.