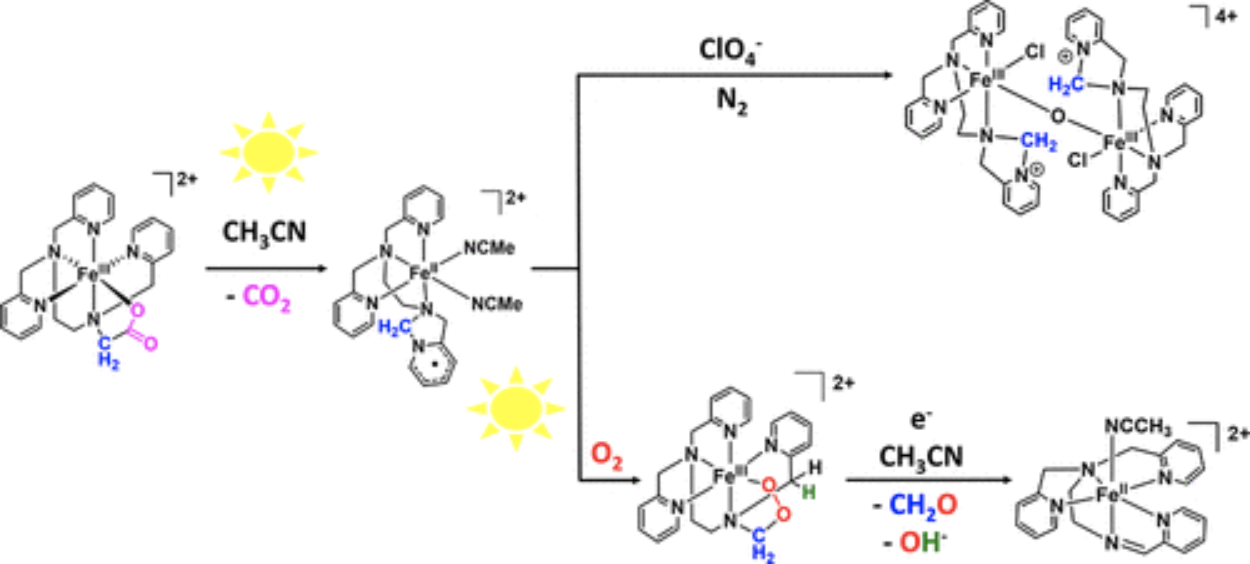
The high-spin (S = 5/2) meridional diastereoisomer of [FeIII(tpena)]2+ (tpena = N,N,N′-tris(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylendiamine-N′-acetate), mer-[Fe(tpena)]2+, undergoes photolytic CO2 release to produce an iron(II) intermediate of a radical dihydroimidazopyridine ligand (L•). The structure of this unprecedented transient iron(II)(L•) complex is supported by UV–vis and Mössbauer spectroscopies, DFT calculations, as well as the X-ray structural characterization of an μ-oxo iron(III) complex of the oxidized derivative of L•, namely, [FeIII2O(Cl)2(L+)2](ClO4)4(MeCN)2 (L+ = 2-(2-(bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino)ethyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo[1,5-a]pyridin-4-ium). [FeIII2O(Cl)2(L+)2]4+ is obtained only in the absence of O2. Under aerobic conditions, O2 will intercept the iron(II)(L•) complex to form a putative Fe(III)-alkylperoxide complex which cascades to an iron(II) complex of SBPy3 (SBPy3 = N,N-bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-N-ethyl-2-pyridine-2-aldimine). Thus, through different oxidative pathways, the unknown ligand L+ or SBPy3 forms by loss of a one-carbon-atom or a two-carbon-atom unit, respectively, from the glycyl arm of tpena. Acceleration of the photodecarboxylation step is achieved by addition of thiocyanate because of transient formation of a more photoreactive NCS– adduct of [Fe(tpena)]2+. This has allowed for kinetic observation of the reaction of [FeII(L•)]2+ with O2 which is, unexpectedly, promoted also by light. We propose that this corresponds to the energy needed for the conversion of the ring-closed radical ligand L• to a ring-opened tautomer to allow for O2 insertion between the C and Fe atoms of the iron(II) complex.