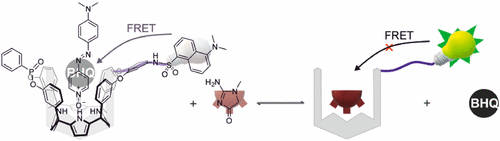
Calix[4]pyrrole phosphonate-cavitands were used as receptors for the design of supramolecular sensors for creatinine and its lipophilic derivative hexylcreatinine. The sensing principle is based on indicator displacement assays of an inherently fluorescent guest dye or a black-hole quencher from the receptor’s cavity by means of competition with the creatinine analytes. The systems were thermodynamically and kinetically characterized regarding their 1:1 binding properties by means of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H and 31P NMR), isothermal titration calorimetry, and optical spectroscopies (UV/vis absorption and fluorescence). For the use of the black-hole indicator dye, the calix[4]pyrrole was modified with a dansyl chromophore as a signaling unit that engages in Förster resonance energy transfer with the indicator dye. The 1:1 binding constants of the indicator dyes are in the range of 107 M–1, while hexylcreatinine showed values around (2–4) × 105 M–1. The competitive displacement of the indicators by hexylcreatinine produced supramolecular fluorescence turn-on sensors that work at micromolar analyte concentrations that are compatible with those observed for healthy as well as sick patients. The limit of detection for one of the systems reached submicromolar ranges (110 nM).