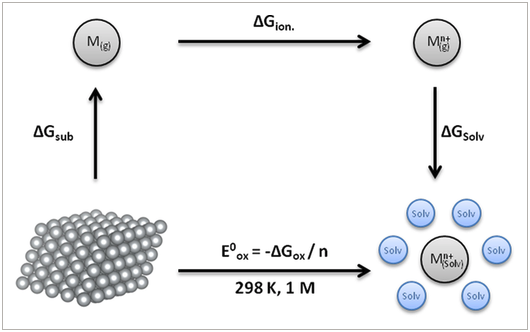
The performance of a thermodynamic cycle for the calculation of the standard reduction potential (SRP) of a series of metals is examined. It is found that the introduction of simple entropic corrections substantially improves the agreement with experimental data. The accuracy of the estimations is in the range of 0.04 V, which opens the possibility to calculate the SRP for metals in non-aqueous solvents or other unusual situations.