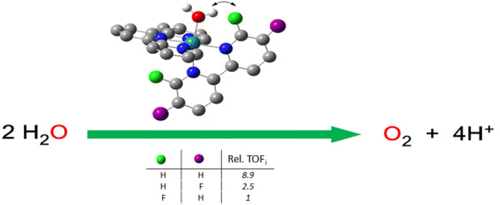
New mononuculear complexes of the general formula [Ru(trpy)(n,n′-F2-bpy)X]m+ [n = n′ = 5, X = Cl (3+) and H2O (52+); n = n′ = 6, X = Cl (4+) and H2O (62+); trpy is 2,2′:6′:2″-terpyridine] have been prepared and thoroughly characterized. The 5,5′- and 6,6′-F2-bpy ligands allow one to exert a remote electronic perturbation to the ruthenium metal center, which affects the combination of species involved in the catalytic cycle. Additionally, 6,6′-F2-bpy also allows through-space interaction with the Ru-O moiety of the complex via hydrogen interaction, which also affects the stability of the different species involved in the catalytic cycle. The combination of both effects has a strong impact on the kinetics of the catalytic process, as observed through manometric monitoring.