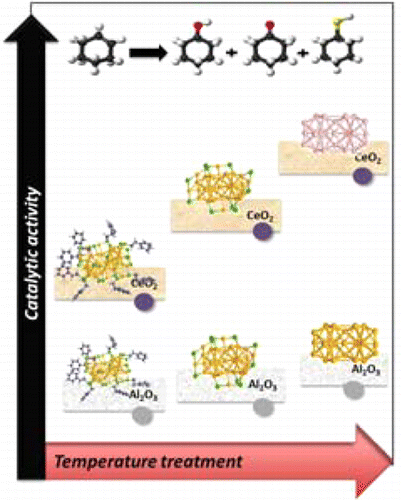
We investigate the distinctly different interaction of thiolate-protected cluster Au38(SC2H4Ph)24with two diverse support materials Al2O3 and CeO2. The catalytic surfaces have been heated in different atmospheres, and the removal of the thiolate ligands has been studied. Thermogravimetry (TG), temperature-programmed process coupled with mass spectrometer (TPRDO-MS), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAFS) studies were performed to understand the desorption of thiol ligands depending on conditions and support material. Depending on the atmosphere and the support material the fate of the thiol ligands is different upon heating, leading to metallic Au in the case of Al2O3 and to cationic Au with CeO2. The thiolate removal seems to be a two-step procedure. The catalytic activity of these Au38-supported clusters was studied for the aerobic oxidation of cyclohexane. Conversion was higher for the gold clusters supported on CeO2. Surprisingly, a significant amount of cyclohexanethiol was found, revealing the active participation of the thiolate ligand in catalytic reactions. The observation also indicates that breaking and formation of C–S bonds can be catalyzed by the gold clusters.