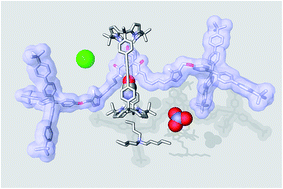
In this work, we report our investigations on the synthesis of a [2]rotaxane based on a bis(calix[4]pyrrole) cyclic component and a 3,5-bis-amidepyridyl-N-oxide derivative axle. We isolated the [2]rotaxane in a significant 50% yield through an optimized “in situ” capping strategy using the copper(I)-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition reaction. The synthetic precursor of the [2]rotaxane, featuring [2]pseudorotaxane topology, could be quantitatively assembled in solution in the presence of one equivalent of tetrabutylammonium chloride or cyanate salts producing a four-particle aggregate. However, we observed that the addition of the salt was deleterious not only for the isolation of the [2]rotaxane in its pure form but, more important, for the optimal performance of the copper catalyst. We probed the interaction of the prepared [2]rotaxane with tetraalkylammonium salts of chloride, nitrate and cyanate anions by means of 1H NMR titrations and ITC experiments. We show that in chloroform solution the [2]rotaxane functions as an efficient heteroditopic receptor for the salts forming thermodynamically and kinetically highly stable ion-paired complexes with 1 :
: 1 stoichiometry. At millimolar concentration and using 1H NMR spectroscopy we observed that the addition of more than 1 equiv. of the salt induced the gradual disassembly of the 1
1 stoichiometry. At millimolar concentration and using 1H NMR spectroscopy we observed that the addition of more than 1 equiv. of the salt induced the gradual disassembly of the 1 :
: 1 complex of the [2]rotaxane and the concomitant formation of higher stoichiometry aggregates i.e. 2
1 complex of the [2]rotaxane and the concomitant formation of higher stoichiometry aggregates i.e. 2 :
: 1 complexes.
1 complexes.