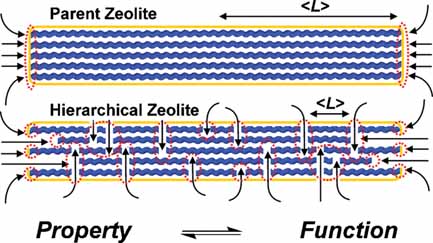
The introduction of mesoporosity in zeolites is often directly coupled to changes in their overall catalytic performance without the detailed assessment of other key functions required for the rational design of the catalytic process such as accessibility, adsorption, and transport. This study presents an integrated approach to study property-function relationships in hierarchical zeolites. Accordingly, desilication of the 1D ITQ-4 zeolite in alkaline medium is applied to develop different degrees of mesoporosity. Along with porosity modification, significant changes in composition, structure, and acidity occur. Relationships are established between the physicochemical properties of the zeolites and their characteristics in the adsorption and elution of light hydrocarbons (C2 to C5, alkanes and alkenes) as well as in the catalytic activity in low-density polyethylene (LDPE) pyrolysis. The recently introduced hierarchy factor can appropriately relate porosity changes to catalytic performance.