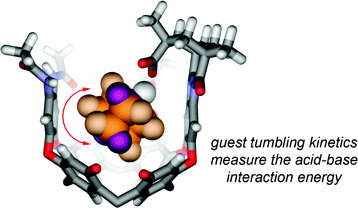
The use of capsules and cavitands in physical organic chemistry is briefly reviewed, and their application to the study of salt bridges is introduced. Carboxylate/ammonium ion pairs are generated within an environment that more or less surrounds the functional groups within a synthetic fixed introverted solvent sphere. This is provided by cavitands that fold around amines and present them with a carboxylic acid function. Both organic and water-soluble versions were prepared, and their equilibrium affinities with quinuclidine bases were determined by NMR methods. The association constants range from approximately 103 M-1 in water to more than 105 M-1 in organic solvents. Studies of nitrogen inversion and tumbling of [2.2.2]-diazabicyclooctane within the introverted acids also illustrate the strength of the acid-base interactions. The barriers to in-out exchange of several amine guests were determined to be in the range from 15 to 24 kcal mol-1. Some parallels with enzymes are drawn: the receptor folds around the guest species; presents them with inwardly directed functionality; and provides a generally hydrophobic environment and a periphery of secondary amide bonds.