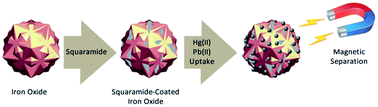
The synthesis and binding properties of squaramide-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles upon coordination with heavy metals in water are described. The nanoparticles feature selective binding towards Hg2+ and Pb2+ cations in the presence of other interfering heavy metals. The binding affinity of the nanoparticles is especially high for mercury and lead cations. The mode of action of the squaramide-coated nanoparticles differs significantly from that of previously reported nanoparticles used as Hg2+ scavengers. The selective Hg2+ sequestering capabilities displayed by the squaramide-coated nanoparticles are related to the formation of organomercury compounds. The solid state structure of the organomercury complex obtained by treatment of a di-squaramide with Hg2+ salts is described, demonstrating the mercuriation of the aryl moiety of dopamine.