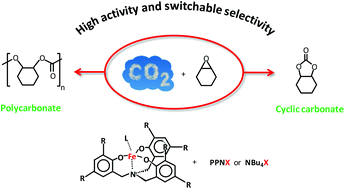
Iron(III) amino triphenolate complexes were studied as catalysts for the reaction of carbon dioxide (CO2) with cyclohexene oxide, which can lead to the formation of cyclic carbonate and/or polycarbonate products. Both types of compound are relevant, but for their practical application it is crucial to be able to control the selectivity of the reaction. By working under solvent-free, green conditions with CO2 in the supercritical state and by tailoring the nature and the relative amount of the co-catalyst (Bu4NX or PPNX, where X is a halide) used in combination with the iron(III) complex, we have been able to enhance the catalytic efficiency and achieve a selective and high-yield synthesis of either the cyclic or the polymeric product. The studied reaction is relevant in the context of green chemistry as it provides an atom-efficient route for the conversion of CO2, which is an inexpensive, widely available, renewable and non-toxic feedstock, into valuable products.