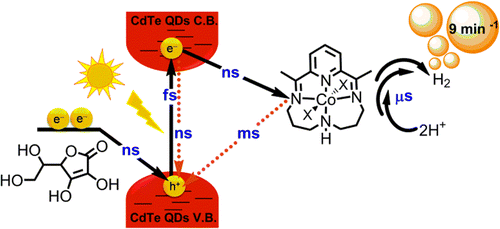
Hydrogen produced from water and solar energy holds much promise for decreasing the fossil fuel dependence. It has recently been proven that the use of quantum dots as light harvesters in combination with catalysts is a valuable strategy to obtain photogenerated hydrogen. However, the light to hydrogen conversion efficiency of these systems is reported to be lower than 40%. The low conversion efficiency is mainly due to losses occurring at the different interfacial charge-transfer reactions taking place in the multicomponent system during illumination. In this work we have analyzed all the involved reactions in the hydrogen evolution catalysis of a model system composed of CdTe quantum dots, a molecular cobalt catalyst and vitamin C as sacrificial electron donor. The results demonstrate that the electron transfer from the quantum dots to the catalyst occurs fast enough and efficiently (nanosecond time scale), while the back electron transfer and catalysis are much slower (millisecond and microsecond time scales). Further improvements of the photodriven proton reduction should focus on the catalytic rate enhancement, which should be at least in the hundreds of nanoseconds time scale.