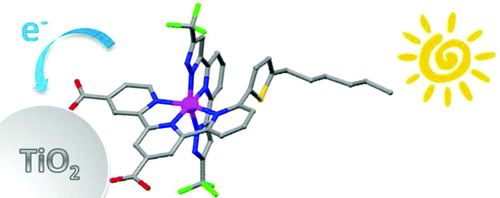
Dicarboxyterpyridine chelates with π-conjugated pendant groups attached at the 5- or 6-position of the terminal pyridyl unit were synthesized. Together with 2,6-bis(5-pyrazolyl)pyridine, these were used successfully to prepare a series of novel heteroleptic, bis-tridentate Ru(II) sensitizers, denoted as TF-11-14. These dyes show excellent performance in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSCs) under AM1.5G simulated sunlight at a light intensity of 100 mW cm-2 in comparison with a reference device containing [Ru(Htctpy)(NCS)3][TBA]3 (N749), where H3tctpy and TBA are 4,4′,4″-tricarboxy-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine and tetra-n-butylammonium cation, respectively. In particular, the sensitizer TF-12 gave a short-circuit photocurrent of 19.0 mA cm-2, an open-circuit voltage (VOC) of 0.71 V, and a fill factor of 0.68, affording an overall conversion efficiency of 9.21%. The increased conjugation conferred to the TF dyes by the addition of the π-conjugated pendant groups increases both their light-harvesting and photovoltaic energy conversion capability in comparison with N749. Detailed recombination processes in these devices were probed by various spectroscopic and dynamics measurements, and a clear correlation between the device VOC and the cell electron lifetime was established. In agreement with several other recent studies, the results demonstrate that high efficiencies can also be achieved with Ru(II) sensitizers that do not contain thiocyanate ancillaries. This bis-tridentate, dual-carboxy anchor configuration thus serves as a prototype for future omnibearing design of highly efficient Ru(II) sensitizers suited for use in DSCs.