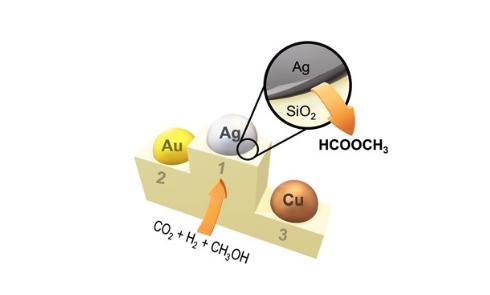
Methyl formate synthesis by hydrogenation of carbon dioxide in the presence of methanol offers a promising path to valorize carbon dioxide. However, how this reaction is driven and what hinders the development of better catalysts for this conversion process still remain unclear. In this work, silica-supported silver nanoparticles are shown to be a significantly more active catalyst for the continuous methyl formate synthesis than the known gold and copper counterparts, and the origin of the unique reactivity of Ag is clarified. Transient in situ and operando vibrational spectroscopy and DFT calculations shed light on the reactive intermediates and reaction mechanisms: a key feature is the rapid formation of surface chemical species in equilibrium with adsorbed carbon dioxide. Such species is assigned to carbonic acid interacting with water/hydroxyls on silica and promoting the esterification of formic acid with adsorbed methanol at the perimeter sites of Ag on SiO2 to yield methyl formate. This study highlights the importance of employing combined methodologies to verify the location and nature of active sites and to uncover fundamental catalytic reaction steps taking place at metal-support interfaces.