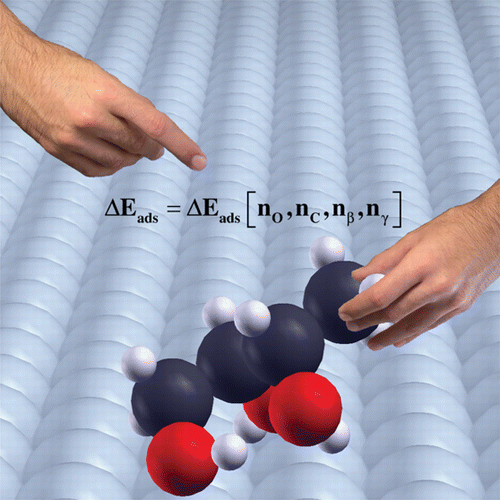
Linear-scaling relationships are powerful tools in the rational design of new catalysts. Few of these thermodynamic relationships consider multifunctionalized molecules, and none deal with intramolecular interactions such as hydrogen bonds, widely present in polyoxygenated molecules obtained from renewable sources. We have completed an adsorption database with 14 mono- and polyalcohols up to four carbon atoms, on clean Pt and Pd(111) surfaces, using periodic density functional theory, and including van der Waals terms, and we have obtained results that are in good agreement with experimental data. With this data, we propose a robust multifactorial linear-scaling relationship, which is an additive function of the contributions from hydroxyl and CHx groups and the hydrogen bonds. We have validated the model by comparison with experiments and by the prediction of adsorption energies of C4–C7 sugar alcohols on both surfaces. Our study paves the way for the study of large multifunctionalized molecules, like those derived from biomass.