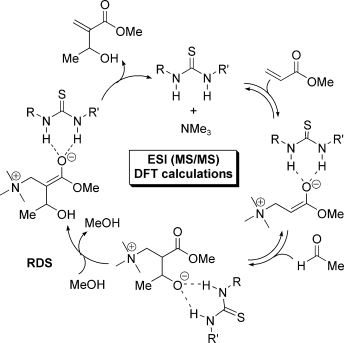
A Morita-Baylis-Hillman (MBH) reaction catalyzed by thiourea was monitored by ESI-MS(/MS) and key intermediates were intercepted and characterized. These intermediates suggest that thiourea acts as an organocatalyst in all steps of the MBH reaction cycle, including the rate-limiting proton-transfer step. DFT calculations, performed for a model MBH reaction between formaldehyde and acrolein with trimethylamine as base and in the presence or the absence of thiourea, suggest that thiourea accelerates MBH reactions by decreasing the transition-state (TS) energies through bidentate hydrogen bonding throughout the whole catalytic cycle. In the rate-limiting proton-transfer step, the thiourea acts not as a proton shuttle, but as a Brønsted acid stabilizing the basic oxygen center that is formed in the TS.