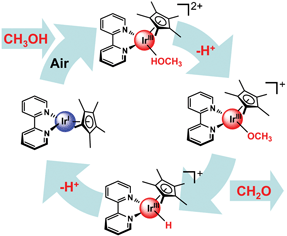
[Cp*Ir(H)(bpym)]+ and [Cp*Ir(H)(bpy)]+ are the first examples of iridium based catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols; the catalytic cycle proceeds via acidic hydrides. Deprotonation of the hydride leads to a highly oxygen sensitive IrI species that regenerate the IrIII complexes upon oxidation with dioxygen.